Library QC¶
At step Removig PCR duplicates you used the flag --output-stats, generating a stats file in addition to the pairsam output (e.g. –output-stats stats.txt). The stats file is an extensive output of pairs statistics as calculated by pairtools, including total reads, total mapped, total dups, total pairs for each pair of chromosomes etc’. Although you can use directly the pairtools stats file as is to get informed on the quality of the Omni-C library, we find it easier to focus on a few key metrics. We include in this repository the script get_qc.py that summarize the paired-tools stats file and present them in percentage values in addition to absolute values.
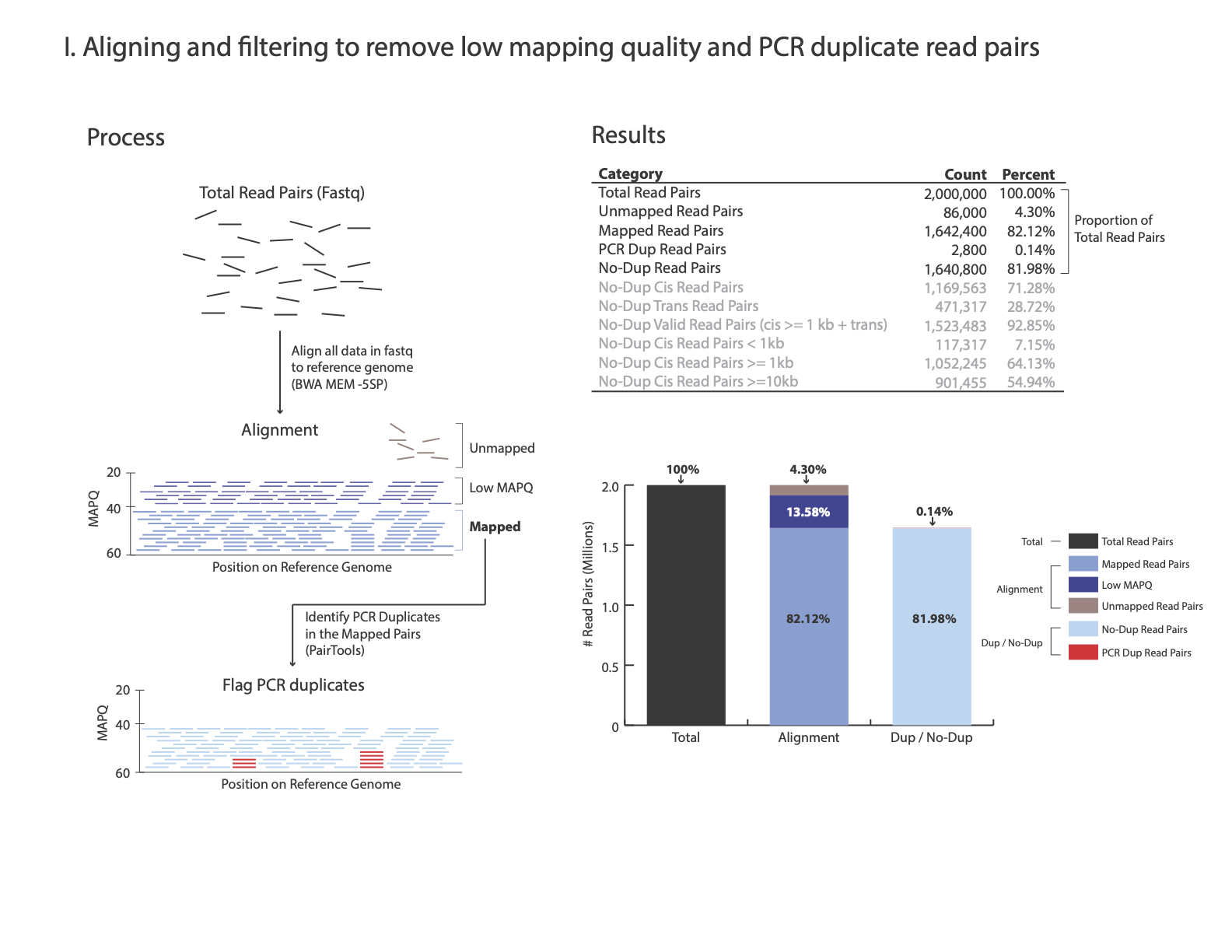
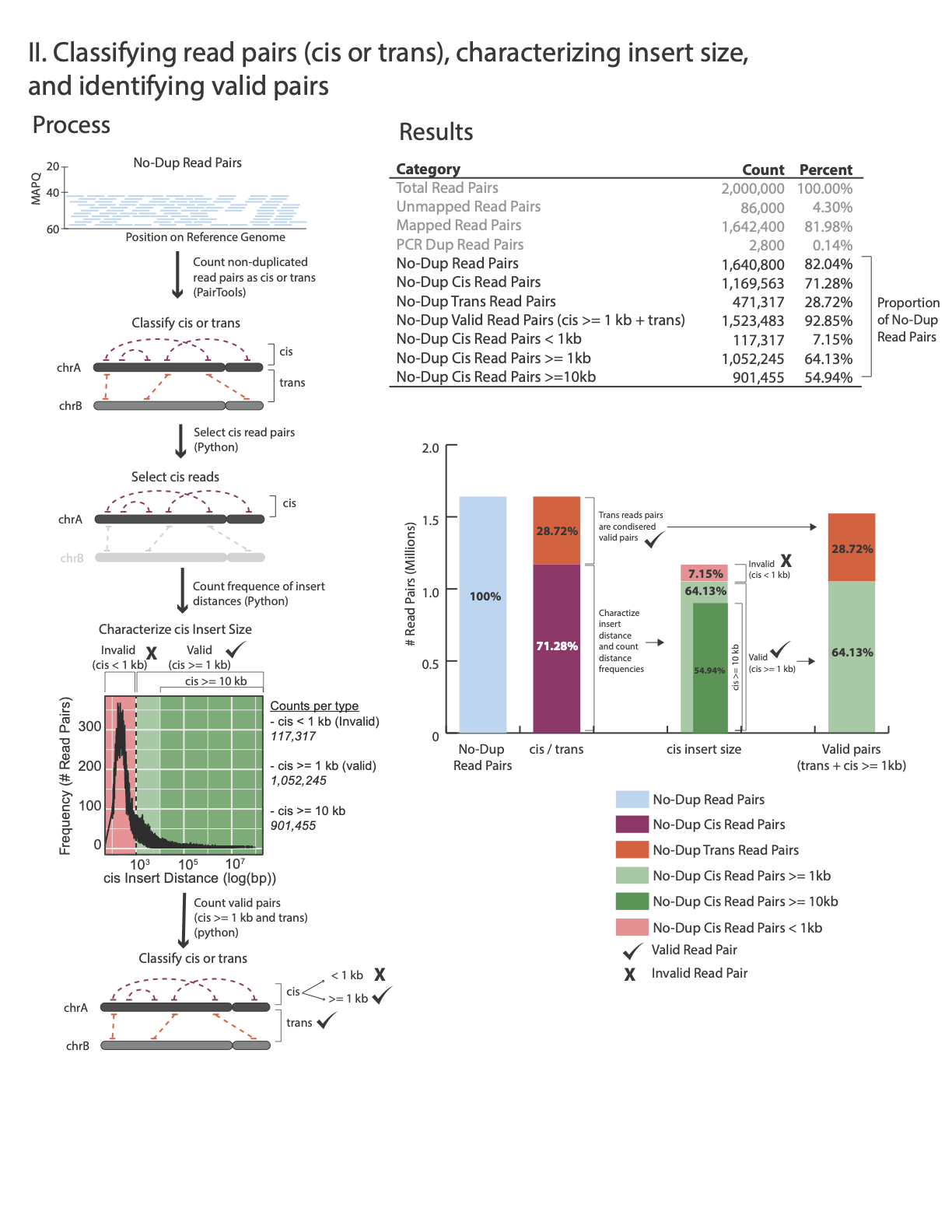
The images below explains how the values on the QC report are calculated:
Command:
python3 ./Omni-C/get_qc.py -p <stats.txt>
Example:
python3 ./Omni-C/get_qc.py -p stats.txt
After the script completes, it will print:
Total Read Pairs 2,000,000 100%
Unmapped Read Pairs 92,059 4.6%
Mapped Read Pairs 1,637,655 81.88%
PCR Dup Read Pairs 5,426 0.27%
No-Dup Read Pairs 1,632,229 81.61%
No-Dup Cis Read Pairs 1,288,943 78.97%
No-Dup Trans Read Pairs 343,286 21.03%
No-Dup Valid Read Pairs (cis >= 1kb + trans) 1,482,597 90.83%
No-Dup Cis Read Pairs < 1kb 149,632 9.17%
No-Dup Cis Read Pairs >= 1kb 1,139,311 69.8%
No-Dup Cis Read Pairs >= 10kb 870,490 53.33%
Library Complexity¶
If you preformed a shallow sequencing experiment (e.g. 2M reads) and running a QC analysis to decide which library to use for deep sequencing (DS), it is recommended to evaluate the complexity of the library before moving to DS.
The lc_extrap utility of the preseq package aims to predict the complexity of sequencing libraries.
preseq options:
Parameter |
Value |
Function |
|---|---|---|
bam |
Specifies that the input file type is bam. Please note that for a bam file to be a recognized input file htslib sould be installed as well and preseq should be built with htslib support (for more details see preseq documentation or our installDep.sh script as example) |
|
pe |
Specifies that paired end data is used |
|
extrap |
2.10E+09 |
Maximum extrapolation |
step |
1.00E+08 |
Extrapolation step size |
seg_len |
1000000000 |
maximum segment length when merging paired end bam |
output |
output file |
Please note that the input bam file should be a version prior to dups removal.
preseq lc_extrap command example for extrapolating library complexity:
Command:
preseq lc_extrap -bam -pe -extrap 2.1e9 -step 1e8 -seg_len 1000000000 -output <output file> <input bam file>
Example:
preseq lc_extrap -bam -pe -extrap 2.1e9 -step 1e8 -seg_len 1000000000 -output out.preseq mapped.bam
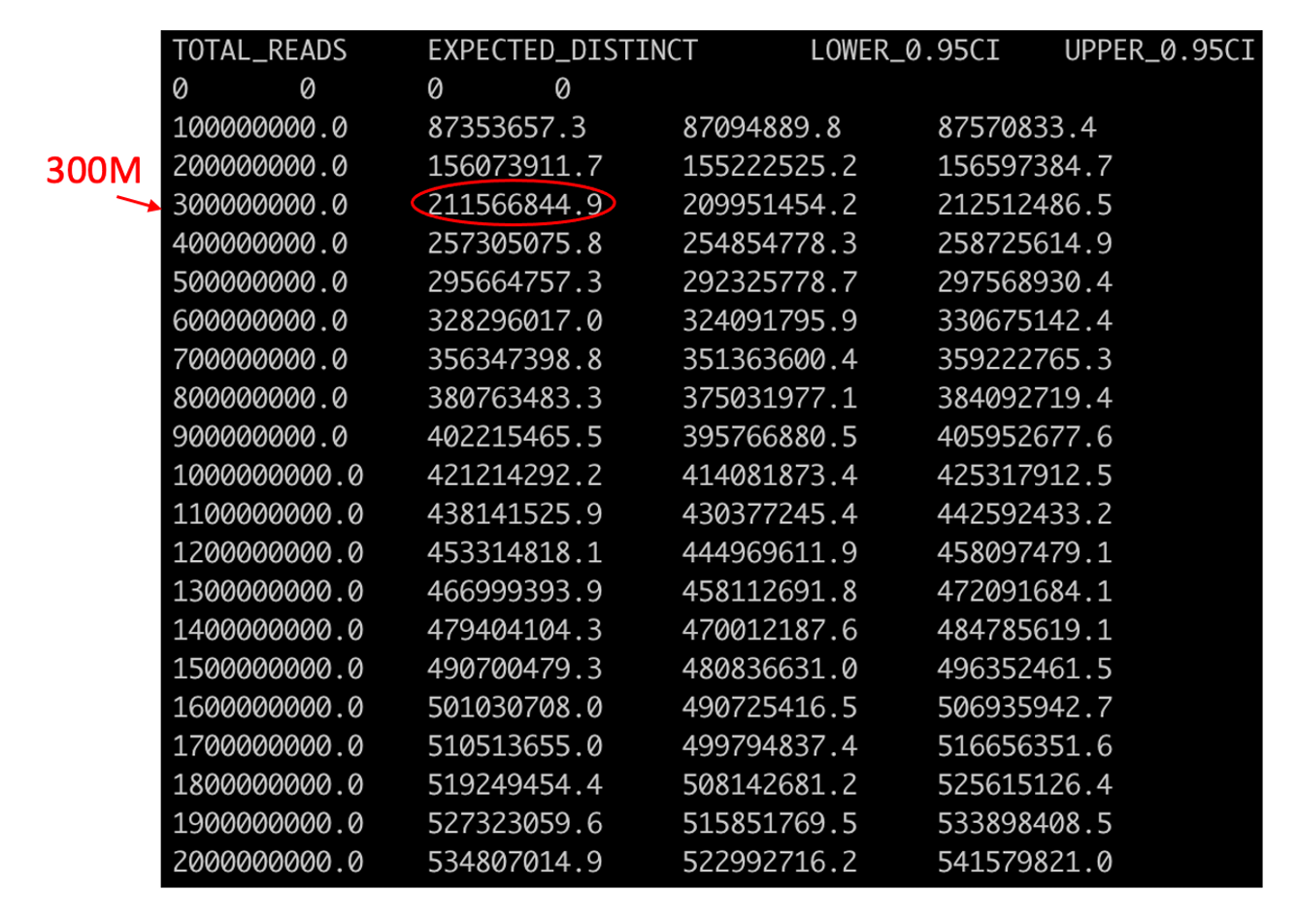
In this example the output file out.preseq will detail the extrapolated complexity curve of your library, with the number of reads in the first column and the expected distinct read value in the second column. For a typical experiment (human sample) check the expected complexity at 300M reads (to show the content of the file, type cat out.preseq). Expected unique pairs at 300M sequencing is at least ~ 120 million.